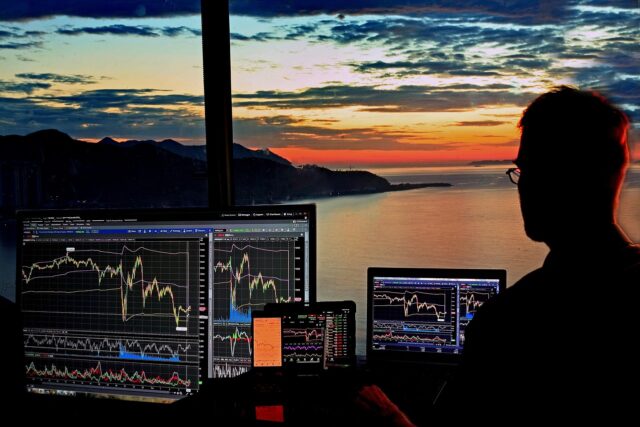
Leverage mechanisms embedded in sophisticated trading platforms enable expert traders to optimize capital efficiency when handling derivatives. The review of margin requirements alongside the various order types offered is critical for managing risk and maximizing returns, particularly in volatile futures markets. This guide provides an in-depth analysis of the major variants of margin contracts, highlighting how each platform tailors these to different strategic objectives.
Futures contracts represent a fundamental pillar of advanced trading systems:, allowing traders to gain exposure while employing leverage effectively. Understanding the subtle differences in order execution – from limit and market orders to stop and iceberg orders – directly impacts trade outcomes. This comprehensive review surveys how each platform integrates these types through unique matching engines and risk controls, influencing liquidity and slippage.
Real-world data confirms that platforms emphasizing robust security mechanisms and low-latency execution excel in arbitrage and intraday strategies. For example, exchanges with tiered margin models demonstrate superior capital efficiency, facilitating high-level strategies such as cross-margining. This expert guide also highlights emerging trends in contract design and margin calculation formulas that promise to redefine users’ approach to leveraged futures trading.
Review of Advanced Trading Platforms
For expert traders engaging with derivatives and futures, selecting trading platforms equipped with sophisticated order types and margin mechanisms is paramount. High-level systems provide a comprehensive guide to managing variants of orders, from limit and stop to iceberg and TWAP, each designed to optimize execution and reduce slippage under different market conditions. Leading platforms integrate in-depth analysis tools that enable users to assess leverage impact on margin requirements and contract volatility, enhancing risk management strategies.
Modern trading platforms excel in delivering multi-layered functionalities that facilitate seamless futures contracts trading with flexible leverage settings. These platforms incorporate advanced algorithms to support complex order types such as bracket and OCO (One Cancels the Other), offering traders granular control over entry and exit points. The integration of real-time order book data and order flow analytics allows for proactive decision-making based on market microstructure and liquidity dynamics.
Margin and Leverage Mechanisms
Understanding margin systems is critical when operating with leveraged futures contracts. Top-tier platforms offer both cross-margin and isolated margin options, enabling traders to tailor risk exposure per position. The margin calculation engines are transparent, providing instant feedback on margin utilization and liquidation thresholds. This clarity is essential to prevent unexpected margin calls in volatile markets, especially when trading derivatives with high leverage ratios.
Platform Security and Execution Efficiency
Security protocols in advanced trading systems now include multi-factor authentication, cold storage for crypto-assets, and encrypted API integrations to prevent unauthorized access and ensure order integrity. Execution speed, measured in milliseconds, is a decisive factor–platforms equipped with low-latency matching engines reduce slippage significantly during high-frequency trades. Case studies from leading exchanges illustrate how optimized order routing and depth of market data reduce risks associated with price manipulation and front-running.
Margin Trading Risk Management
Effective risk management in margin trading requires the disciplined use of leverage mechanisms tailored to the specific derivatives and futures contracts available on sophisticated trading platforms. Risk exposure can be minimized by combining stop-loss and take-profit orders alongside advanced order types such as trailing stops and conditional orders. Employing these systems optimizes position sizing and reduces liquidation probability, especially when managing high-level order variants in volatile markets.
Platforms offering a comprehensive suite of risk management tools enable traders to define rigorous margin requirements and maintenance levels, allowing for real-time monitoring of margin calls and automatic position adjustments. Expert analysis indicates that integrating these mechanisms with algorithmic trading systems enhances precision, helping traders avoid overleverage despite the temptations presented by high leverage ratios inherent in futures trading.
Order Types and Leverage Controls
Advanced order types form the backbone of proactive risk mitigation. Using limit orders combined with conditional triggers ensures entries and exits align with pre-established risk thresholds. Among variants of derivatives contracts, perpetual futures often carry distinct margin and funding rate structures which require constant assessment via platform systems to maintain sustainable exposure. Leverage controls should be dynamically adjusted according to market liquidity, volatility, and the underlying asset’s behavior, a practice supported by in-depth platform review reports.
Security and System Reliability
Risk management extends beyond position control into platform security and operational integrity. Leading trading platforms incorporate redundant systems and real-time surveillance to detect anomalous trading activities and potential security threats, safeguarding funds against rapid losses from liquidation or market manipulation. Case studies of exchanges equipped with robust margin and futures trading systems demonstrate significant reduction in forced liquidations during market crashes, highlighting the value of comprehensive, high-level risk frameworks embedded in the design of advanced trading platforms.
Futures Contracts Settlement Process
To ensure accurate risk management and capital allocation in futures trading, understanding the settlement process is fundamental. Futures contracts settle either via physical delivery or cash settlement, with the majority of crypto derivatives platforms opting increasingly for cash mechanisms to enhance liquidity and operational efficiency.
Physical delivery requires traders to exchange the underlying asset at contract expiration, necessitating robust infrastructure and compliance systems within platforms. This variant suits commodities but is less common in digital asset futures, where settlement typically occurs in the contract’s reference currency. Cash settlement calculates the difference between the contract price and the settlement price on expiry, crediting or debiting trader accounts accordingly.
Settlement Price Determination
Platforms employ specific mechanisms to determine the official settlement price, often using a volume-weighted average price (VWAP) from underlying spot markets or a composite index aggregated from multiple exchanges. For example, major platforms like Binance Futures use an index derived from top spot markets to minimize price manipulation risks and maintain fairness in margin calculations across variants of futures contracts.
- Mark-to-Market Settlement: Margin accounts undergo daily settlement where unrealized profits and losses adjust balances, maintaining leverage within platform-defined thresholds.
- Final Settlement: Occurs at contract expiration, closing open positions based on the settlement price, affecting margin and collateral requirements.
Risk Mitigation and Systemic Considerations
Advanced trading platforms incorporate sophisticated liquidation engines triggered when margin levels fall below maintenance thresholds during settlement, preventing cascading defaults. The settlement process integrates with order book and margin systems to execute forced closures or partial position reductions, ensuring platform solvency.
- Automated clearing mechanisms reconcile open positions and cash flows.
- Transparent settlement data feeds support in-depth analysis and audit trails for regulatory compliance.
- Systems continuously monitor settlement variants and order types to dynamically adjust leverage caps and margin requirements.
In-depth familiarity with these settlement mechanics enables expert traders to optimize strategies around contract expiries, minimizing slippage and capital inefficiency. The evolving sophistication of settlement systems remains pivotal for those aiming to leverage futures derivatives effectively in high-level trading environments.
Order Types Execution Strategies
Optimal execution in futures trading requires a precise understanding of order types and the mechanisms each platform offers. Market, limit, stop, and conditional orders represent the core variants utilized by expert traders to control entry and exit points with precision. Platforms provide differing implementations of these types, impacting slippage, fill rates, and exposure to adverse price movements. For example, aggressive market orders ensure immediate execution but risk high slippage on volatile futures contracts, whereas limit orders facilitate price control at the expense of execution certainty.
Leveraging sophisticated order types such as iceberg and TWAP (Time-Weighted Average Price) orders enables high-level execution strategies tailored for large volumes and reduced market impact. Iceberg orders hide true order size, preventing information leakage that might influence derivatives prices, a crucial factor on high-leverage margin platforms. TWAP algorithms distribute orders over a specified time horizon, improving execution quality by smoothing market impact and reducing transaction costs. An in-depth analysis of system capabilities across advanced trading platforms reveals that integration of smart order routing enhances performance by dynamically selecting venues with optimal liquidity and spreads.
Strategic deployment of stop-loss and take-profit orders within margin trading systems reduces downside risks while automating profit capture on futures contracts. Expert guides emphasize setting stop levels in relation to volatility metrics like ATR (Average True Range) to avoid premature stops and leverage price oscillations effectively. Similarly, trailing stops dynamically adjust to favorable price moves, locking profits while permitting upside potential. These mechanisms are integral to comprehensive trading plans combining leverage and risk management without constant manual intervention.
Order execution strategies must adapt to current market microstructure and liquidity conditions, which vary significantly between spot and derivatives systems. For instance, in highly liquid cryptocurrency futures markets, rapid price fluctuations necessitate the use of limit orders combined with conditional triggers to capitalize on arbitrage opportunities or market inefficiencies. Platforms increasingly support API-driven order management, enabling expert users to implement algorithmic strategies that exploit millisecond-level pricing anomalies while maintaining strict security protocols to safeguard margin and account integrity.